Long Term Vs. Short Term Memory
You may remember something that you learned or experienced several years ago: this is long term memory. Unlike short term memory, memories from minutes/hours ago, long term memory refers to distant memories, usually measured from years to decades, and the lasting retention of information and skills.
Long term memories are relatively permanent compared to short term memories. They often happen outside of the conscious mind, and are memories that are frequently accessed and get more and more powerful over time. There are 3 types of long term memories; semantic, episodic, and procedural. All three of these long term memory types gradually erode over the time of having Dementia.
Semantic long term memories are a type of declarative memory – memories that can be explained. They refer specifically to understanding words, and actions. For example, being able to explain the word “Alzheimers”, is a semantic memory.
http://theconversation.com/were-capable-of-infinite-memory-but-where-in-the-brain-is-it-stored-and-what-parts-help-retrieve-it-63386.
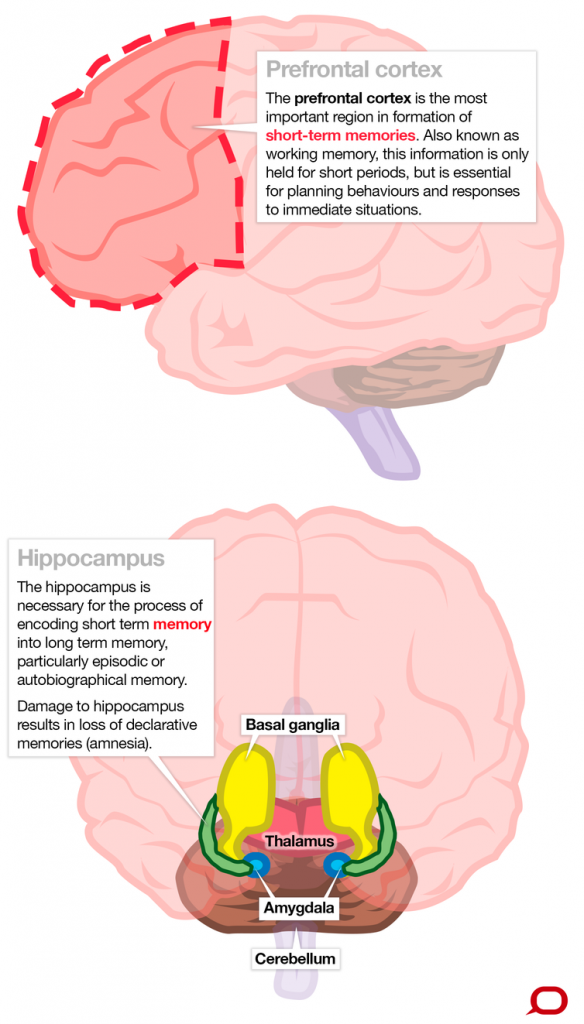
Episodic memories are also a type of declarative memory, though this variety of memories touches on significant events in a person’s life. The vivid memories of your wedding, graduation, and your child being born are all good examples of episodic memory. Episodic memories are found in the hippocampus, and semantic memories are also stored there as well as in the Medial Temporal Lobes (MTL).
Procedural memories are very different in comparison to semantic and episodic memories. They are far more back-breaking to explain – making in a non-declarative memory. Procedural memories encompass how to do something, including the specific footsteps you took to achieve your goal. Though you might “know” how to do a backflip, it’s very hard to explain what makes your back bend the way it does, or how your body balances. They are also encoded in the Putamen, Cerebellum, Motor Cortex and the Caudate Nucleus, which are all involved with motor control. Short term memory is usually found in the temporal lobe of the brain. Both short term and long term memory are associated with the frontal lobe of the brain.
Sadly, long term memory is affected by Dementia, a system of diseases that describes various symptoms of cognitive declines, such as forgetfulness. Often, people who have the first symptoms of Dementia forget short term memories, such as what they ate for breakfast, or forgetting what you said earlier in a conversation. As Dementia progresses long term memories start to fade. This long term memory loss refers to Amnesia.
Works Cited
“Declarative Memory & Procedural Memory: Explicit & Implicit.” The Human Memory, © The Human Memory, 27 Sept. 2019, http://human-memory.net/explicit-implicit-memory/#:~:text=Procedural%20memories%2C%20on%20the%20other,are%20involved%20in%20motor%20control.\.
“Where Are Memories Stored in the Brain?” Queensland Brain Institute, © The University of Queensland, 23 July 2018, http://qbi.uq.edu.au/brain-basics/memory/where-are-memories-stored#:~:text=The%20hippocampus%2C%20located%20in%20the,How%20do%20we%20know%20this%3F.
“SHORT-TERM MEMORY.” THE BRAIN FROM TOP TO BOTTOM, http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_07/d_07_cr/d_07_cr_tra/d_07_cr_tra.html#:~:text=The%20reason%20is%20that%20long,various%20places%20in%20the%20cortex.
Boundless. “Boundless Psychology.” Lumen, http://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-psychology/chapter/memory-and-the-brain/#:~:text=The%20temporal%20lobe%20is%20important,%2D%20and%20long%2Dterm%20memory.

